Network, Protocols and Topologies

Hello everyone with a new blog post! As of 2023, I am continuing the series of blog posts that I have been taking a break for a long time. I am here with the first article of the series consisting of 3 blog posts that we call Network Basics, I wish you good reading in advance.
What is Network?
The first thing we need to know before moving on to network basics is what a network is. So what is Network?
Network is the connection of multiple devices to each other in order to share resources. Network enables sharing of resources between devices in software or hardware. For example, if we take examples from a company network, in an office environment where there is no network, an external storage device is needed to transfer the software resource to another computer. Thanks to the network, this need is met by the reliable and fast transmission of the software resource on a common network where computers are connected without the need for an external media or storage device. Of course, this is a very simplified example of file transfer.
Another way of looking at it is that in environments without a network based on hardware resources, people still need an external media or storage device to transfer the files they need to hardware devices. Thanks to the network, for example, the output you want to get through a printer is very simple and the network can quickly provide you with a solution thanks to the hardware resource support of the network.
Of course, there are some requirements for computers to be connected to each other in networks. For example, there are three different methods used to connect two computers to each other.
- Ethernet,
- Fiber Cable,
- Wireless.
I will cover them in detail later, but I wanted to mention them briefly for the sake of knowledge. So, we have learned what we need to use to connect two or more devices to each other. However, we also need to know the protocols necessary to establish communication between devices. So let’s continue with our next topic, Network Protocols.
What is a Network Protocol?
As everyone knows, people around the world need to know common languages in order to talk to each other and transfer information to each other. Network also works in this way. The network enables communication between two devices, just like people, but first the two devices must be able to speak the same language. Devices in the network can only communicate and transfer information with each other if they use common protocols.
I will examine this issue in the OSI Reference Model, which I will cover in detail in my upcoming blog posts. Let’s continue without slowing down and move on to our next topic, What are Network Topologies?
Network Topologies
It is the topology that determines how devices in a network are placed, how they are connected and how they transmit data. Today, it is used in two different ways. It is divided into two as Physical and Logical topology.
What is Physical Topology?
Physical topology is the topology that determines how the network will physically look like. It determines how the devices and cables in the network should be organized.
What is Logical Topology?
Logical topology utilizes physical topology to determine how data is transferred.
Network engineers need to consider these two topologies when designing a network and place devices and create the network according to these two topologies.
Today, the most widely used and known Network Topologies are the design models developed on five sequences. These models are used by network and system engineers in the required environments.
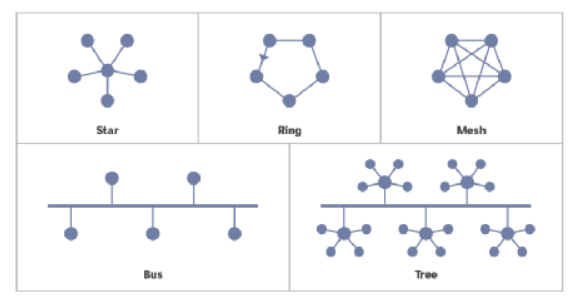
As you can see in the picture, 5 different network topologies are shown. These are
- Bus Topology
- Ring Topology
- Star Topology
- Tree Topology
- Mesh Topology
They are network configurations named as. The topologies here have pros and cons compared to each other. Let us examine them in order.
Bus Topology:
In this topology type, communication between devices takes place on a single line. The data transferred on the network goes to all devices until it is transferred to the target device. For this reason, network performance is very low and is not widely preferred today. In addition, the communication type used on this topology is Ethernet.
This type of topology is very popular as it can be easily installed on the network. In addition, when an additional device is desired to be connected to the network, it can be easily added. It is economical, and it is possible to create a network without the need for external network devices such as switches or hubs.
However, every good thing has some disadvantages. In this topology type, the limited number of devices that can be connected and the limited line length are the main disadvantages.
In addition, in this topology, it is difficult to detect failures or errors in the systems installed on the backbone. In addition, when a problem occurs on the network, all devices connected to the network are affected. The data transfer rate is also low.
Ring Topology:
In this topology type, the data sent on the network is transferred to all devices until it reaches the receiving device. Although it is logically ring-shaped, it actually has similarities with star topology. Although it is logically in the form of a circle, since it physically consists of devices connected to the MAU, it is logically analogized as a ring and physically as a star.
As with the bus topology, there are some advantages and disadvantages here.
The advantages are that all devices on the network have the same authorization and there is little performance degradation if a device is added to the network.
As disadvantages, a malfunction that may occur on a device connected to the network may cause the entire network to become unusable. It is also a very costly topology.
Star Topology:
Star topology consists of a hub or switch in the center and devices connected to it. In this topology, the data is logically sent to the hub or switch before the device from which the data originates. Then the data is transmitted to the destination device.
In this topology, if the network device called hub or switch at the center fails, the connection between the target computers from which the data originates and the target computers to which the data should be transmitted is broken. Ethernet protocol is widely used as a protocol. Devices can also be transmitted via fiber optic cables.
In this type of topology, network management and problem detection is easier, and it is also easy to add new devices. The biggest difference compared to the topologies I have mentioned so far is that a problem occurring in the destination or sender device does not affect the network.
As disadvantages, a problem in the intermediary network device in the center affects the whole network. It also requires more cable connections.
Tree Topology:
In this topology, which we call tree topology, devices are connected to each other with two different connection points. This topology is often used to bring together networks in a star topology structure at an upper connection point. Thus, networks can be scaled up.
The advantages of this topology are that it is easy to reach each device and the segments they form. The device boundary of each intermediate topology is limited by the cable length. When backbone cables or central devices fail, the network is disrupted. It is difficult to install and organize.
Mesh Topology:
In this topology, a device connected to the network is connected to all other devices on the network. In this topology, if a problem occurs on one line, the device can maintain the connection through other lines.
As an advantage, this topology has the biggest advantage with its high data rate. In addition, when a new device is to be added to the network, it can be easily included.
As disadvantages, the number of connections is high. Too many cables are used and the cost is high.
After examining our last topology type, Mesh, we have finished the topics I planned for our first blog post today. Hope to see you in my next blog post.